Platelets and Process of Rejuvenation and Tissue Repair
Platelets and Process of Rejuvenation and Tissue Repair
Platelets, one of three major blood cells, play a key role in natural process of repair, healing and rejuvenation of damaged tissue. The entire process occurs over time by utilizing effects of several factors contained in platelets.
To make it understandable here is the most simplified explanation: a damaged tissue (whether damaged by sun, physical trauma, burn, heart attack or stroke) sends a signal to the rest of your body that help is needed to rescue the area. Many different cells participating in tissue repair, from nearby cells to those circulating in blood, receive the signal and begin aggregating at the site of damage. One of the most important are the platelets, a normal constituent of our blood. Platelets aggregate in damaged area and release the “healing” factors that begin process of reparation. The process is quite long since your body can only bring a limited number of platelets to the damaged site.
PRP is a process of concentrating platelets obtained from your own blood. It requires blood to be span down in a special centrifuge, preferably twice, with red blood cells and white blood cells being discarded. What’s left are very concentrated platelets that are injected to the site of damage. The concentration of platelets in PRP is several times higher than what body can deliver. By enhancing the body’s natural healing capacity, PRP injection leads to a rapid, efficient, and thorough restoration of tissue to its healthy state.
The concentrated platelets contain numerous factors participating in healing, repair, tissue rejuvenation and attracting stem cells to the area of injury. These “healing” factors stimulate proliferation of mesenchymal cells, stimulate extracellular matrix production, including collagen, and increase angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels) allowing rapid healing of injuries.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy has become the ultimate biological treatment for injuries in Sport Medicine , Orthopedic, Cardiovascular Surgery, Oral Surgery and in Veterinary Medicine. Although PRP has made its entry to the Aesthetic Medicine relatively late it has quickly become one of the most effective procedures in skin rejuvenation.
Two major indications for use PRP in Aesthetic Medicine are skin rejuvenation, hair restoration and to extend the longevity of dermal fillers.
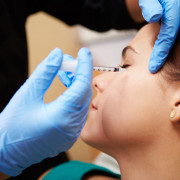
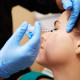
The process involves drawing 2 small tubes of blood and spinning them at the very high centrifugal forces. At the Visage, we spin the blood twice, each time discarding unnecessary components. Once the process is completed the remaining concentrated platelets are transferred to syringes and are ready for injection.
The injections may involve either the areas of concern only or the entire face. Numerous injections, mostly superficial, are spaced 1/2 – 1/3 inches apart.
Following the injections, there is no specific aftercare and you may return to your normal daily activities. The process of rejuvenation has begun
Frequency of PRP injections
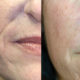
How often to have the PRP injections to achieve the best results depends on the condition of your skin. On average, 4 sessions every 4-6 weeks are optimal with maintenance injections every 8 – 12 months. This method provides the best long term results with no downtime and is apreferred rejuvenation technique for active individuals as well as the celebrities; it has replaced the majority of more aggressive rejuvenation procedure such as the CO2 laser resurfacing.
If the skin sustained a significant chronic sun damage associated with extensive wrinkling and laxity, the PRP injections can be used together with topical application during aggressive micro-needling.
In summary, PRP has become one of very few aesthetic procedures that provides universal benefits to anyone interested in skin rejuvenation. It is 100% natural, does not have any contraindications and no downtime